In the rapidly modernizing B2B landscape, continuously enhancing customer experience (CX) is becoming increasingly crucial.
To provide a more comprehensive view of CX and drive strategic decision-making, this article explores the integration of conventional lagging metrics with newer advanced metrics
When Snowflake's NRR dropped by 47% — and the CEO exited — many wondered if the NRR drop was one of the reasons. Note, 131% NRR is significant and high, but Snowflake's NRR Rate in FY22 Q4 was an industry-leading 178%.

Although, the quarter lower guidance may have been the really reason for the significant market cap drop. Putting th 47% NRR drop in perspective, the median NRR across businesses dropped 10%.

Let's start by saying GRR and NRR are CFO and CRO metrics and GDR and NDR are CFO metrics.
NDR is NRR expressed in US dollars. What rate is used to do the conversion differs.
Further, a global CCO / CRO may also care about NDR, but perhaps a simplified version, known as Constant Currency NDR.
A Global CFO would prefer a transactional-level NDR or an NDR based on daily conversion rate.
Here is a quick recap of GRR, NRR, and how it compares to NDR, from my previous in-depth article.
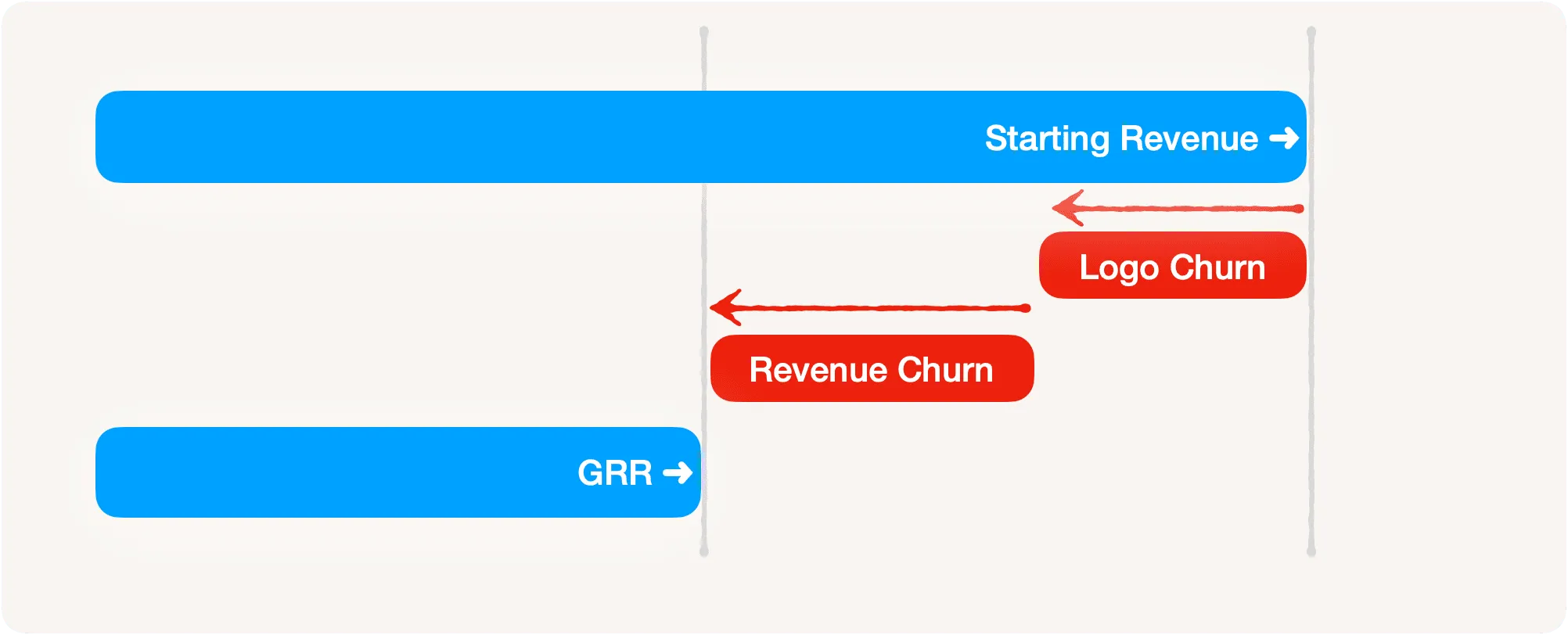
Gross Revenue Retention (GRR) is the revenue at the beginning of the period minus the churn at the end of the period, where churn includes cancellations or logo or customer churn and downgrades or revenue churn.
Revenue churn occurs when the customer stays but pays you less. Logo or customer churn happens when the customer leaves and doesn't renew.
GRR is equal to the starting revenue minus all churn in a period.

If the revenue at the end of June was $4M and customer and revenue churn in July was $300K and $200K,
GRR for July = $4M - $300K - $200K = $3.5M.
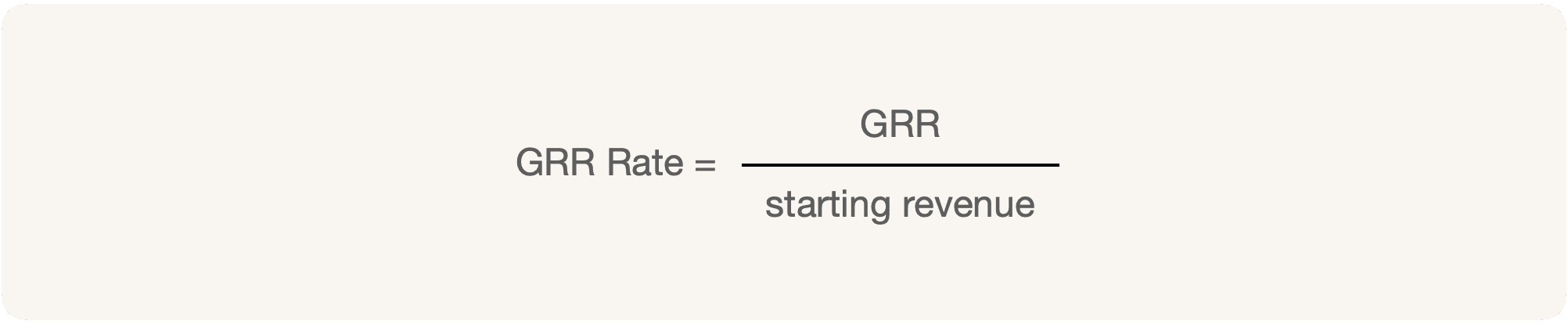
Gross Revenue Retention Rate is the revenue at the beginning of the period minus the customer and revenue churn at the end of the period, divided by the revenue at the beginning of the period.

Continuing with our example, if the revenue at the end of June was $4M and customer and revenue churn in July was $300K and $700K,
GRR Rate = ($4M - $300K - $200K) / 4M = 3.5/4 = 87.5%
Net Revenue Retention (NRR) is the revenue at the beginning of the period minus all the churn (customer and revenue churn) plus all the expansion revenue (upsells or upgrades, cross-sells, and add-ons) in the period.

NRR in terms of GRR is:
NRR = GRR + expansion revenue in period.
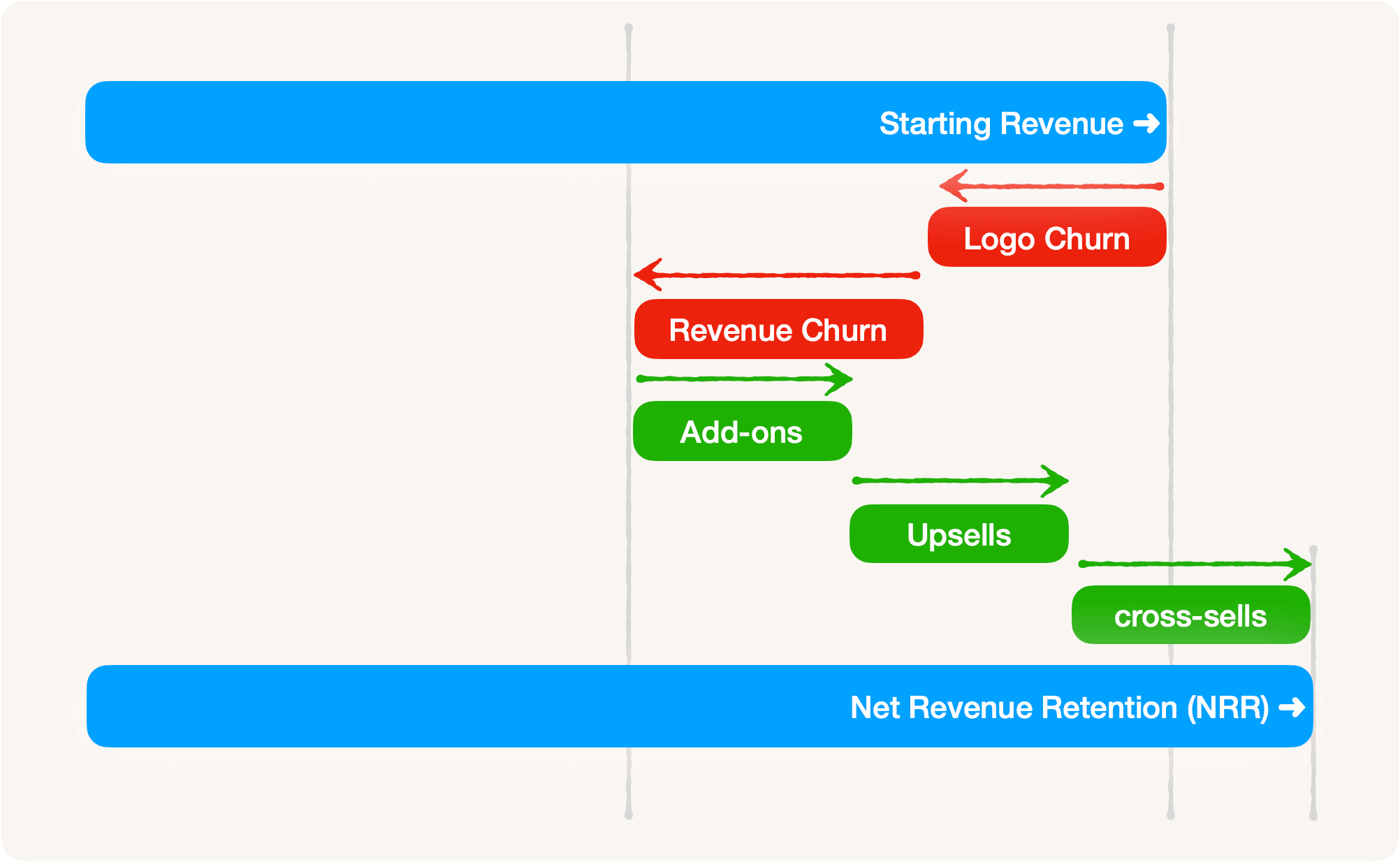
Continuing with our example, if the revenue at the end of June was $4M, customer churn in July was $300K, revenue churn was $200K, and upsells, cross-sells, and add-ons were $600K, $300K, and $100K respectively,
NRR = $4M - $300K - $200K + $600K + $300K + $100K = $4.5M.
Net Revenue Retention Rate is the revenue at the beginning of the period minus the customer and revenue churn plus the upsells or upgrades, cross-sells, and add-ons at the end of the period divided by the beginning revenue.
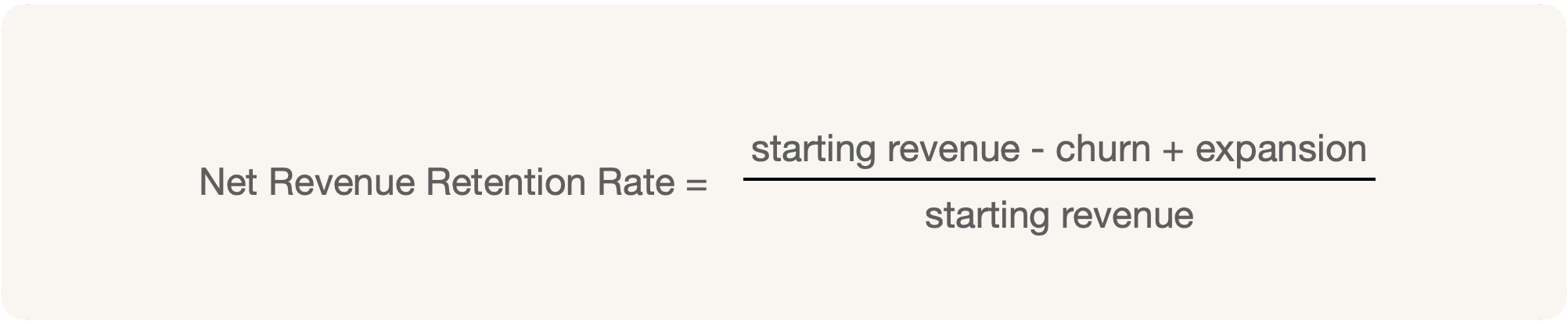

NRR Rate = (GRR + upsells + cross-sells + add-ons) / starting revenue
Continuing with our example, if the revenue at the end of June was $4M, customer churn in July was $300K, revenue churn was $200K, and upsells, cross-sells, and add-ons were $600K, $300K, and $100K respectively,
NRR Rate = ($4M - $300K - $200K + $600K + $300K + $100K)/$4M = 112.5 % or 1.125
Gross Dollar Retention (GDR) is the starting revenue converted to dollars minus the churn converted to dollars both based on the actual exchange rates.

Gross Dollar Retention (GDR) is the starting revenue converted to dollars minus the churn converted to dollars, divided by the starting revenue in dollars, for a given period.
It is the same as the GRR rate, with the difference that all calculations are done in US dollars and it accommodate currency fluctuations.
GDR and GRR differences, i.e., accommodating for currency exchange and fluctuations, are highlighted in S-1 and 10-K reports by public companies. For, customer success, they are the practically same.

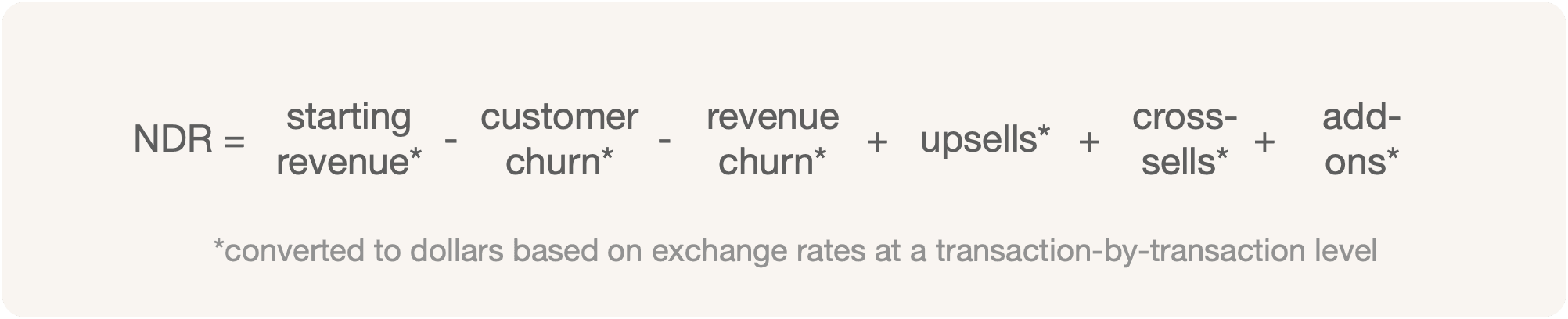
Net Dollar Retention (NDR) is the starting revenue in dollars at the beginning of the period, minus the customer and revenue churn in dollars, plus the upsells or upgrades, cross-sells, and add-ons in dollars. It is essential to highlight that revenue, churn, and expansion are converted into US dollars to accommodate currency translation and exchange rate fluctuations. That is how NDR differs from NRR.
For Customer Success and a SaaS metric to measure and track, Net Dollar Retention (NDR) is the same as Net Revenue Retention (NRR). However, your book-keeping professional obviously will have a different opinion.
For Customer Success Net Dollar Retention (NDR) is the same as Net Revenue Retention (NRR). Your book-keeping professional obviously will have a different opinion.
NRR Rate = NRR / starting revenue (all converted to dollars)
To further illustrate the point, if the revenue at the end of June was $4M, customer churn in July was $300K, revenue churn was $200K, and expansion reveue was as follows:
NDR = $4M - $300K - $200K + (217.38K x 1.38 + 100K + 11,111K / 111 + 71K x 1.41) + $300K + $100K
NDR = $4,500,193
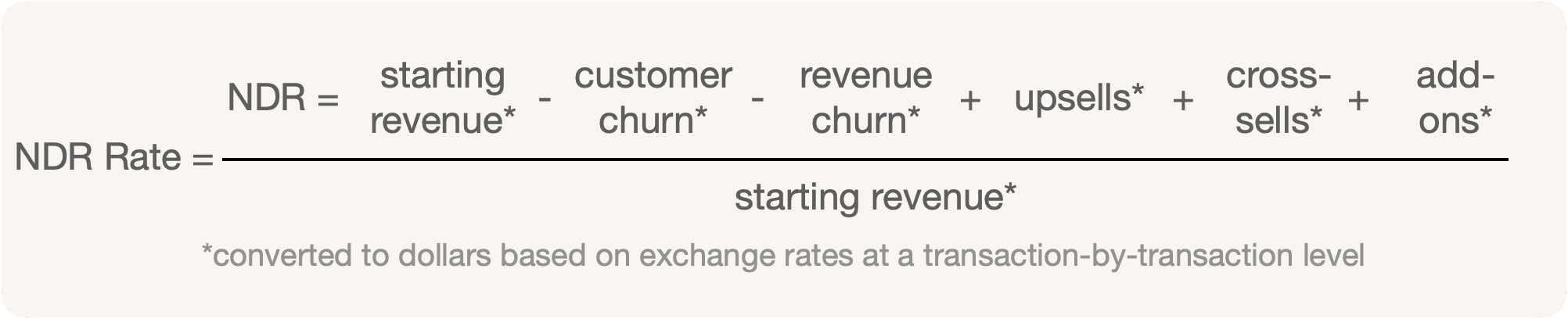
NDR rate = 112.5048%
NDR may use a fixed exchange rate in certain cases to remove the impact of foreign currency translations. It is then differentiated as Constant Currency Dollar-Based NRR or Constant Currency NDR or Constant Currency Dollar-Based Net Expansion Rate (e.g. Agora.io S-1).
In the above example using a constant currency rate of 1.4 for pound to dollar,
Contant Currency NDR = $4M - $300K - $200K + (217.38K x 1.4 + 100K + 11,111K / 111 + 71K x 1.4) + $300K + $100K
Contant Currency NDR = $4,508,831
Contant Currency NDR rate = $4,508,831 / $4M = 112.72%
NRR is a non-financial metric for customer facing execs, for example, for the CCO and CRO.
[Constant Currency] NDR is a metric that a Global CCO or CRO would care more about.
A Variable Currency NDR is something a CFO would care about as is the most accurate representation. the conversion to NDR may be based on a daily average or transactional.
